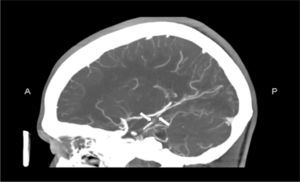
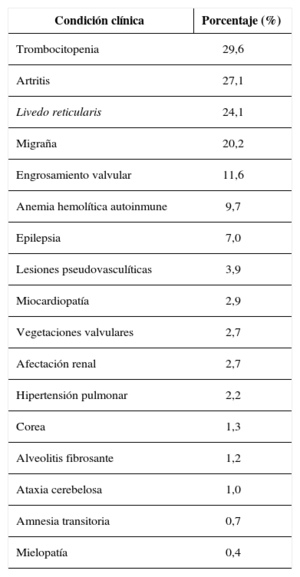
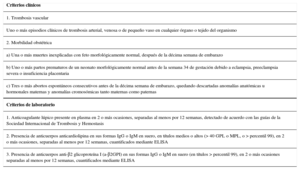
El síndrome antifosfolípido (SAF) se caracteriza por la coexistencia de trombosis (venosas y/o arteriales) y/o pérdidas fetales recurrentes, y la presencia de anticuerpos antifosfolípidos circulantes, principalmente anticoagulante lúpico, anticuerpos anticardiolipina o anti-b2 glicoproteína I. Puede existir aislado o asociado a otras enfermedades autoinmunes, especialmente lupus eritematoso sistémico. Se considera una enfermedad sistémica y, además de la trombosis y de la morbilidad obstétrica, existen otras manifestaciones clínicas características como la trombopenia, la livedo reticularis, la valvulopatía cardíaca y la nefropatía.
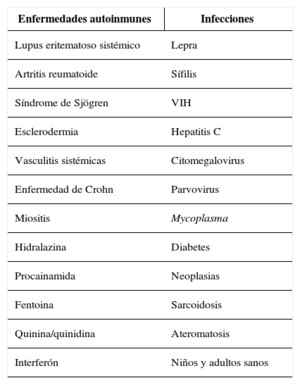
EtiopatogeniaLos mecanismos que llevan a esta situación son desconocidos y probablemente la combinación de varios de ellos de lugar a las manifestaciones del síndrome.
TratamientoEl tratamiento del SAF significa profilaxis: primaria en aquellos pacientes portadores de anticuerpos antifosfolípido asintomáticos y secundaria para prevenir las recurrencias en aquellos que han presentado trombosis previas.
Palabras clave
The antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is characterised by the coexistence of thrombosis (in veins and/or in arteries) and/or recurrent miscarriages, and the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies, mainly lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin or anti-β2 glycoprotein 1 antibodies. It can occur by itself or coexist with other autoimmune diseases, especially systemic lupus erythematosus. It is considered a systemic disease and, besides the thrombosis and obstetric morbidity, there are other characteristic clinical manifestations such as thrombocytopenia, livedo reticularis, heart valve disease and nephropathy.
EtiopathogenesisThe mechanisms that lead to this situation are unknown and it is probably a combination of several of them what trigger the manifestations of the syndrome.
TreatmentAPS treatment involves prophylaxis: primary in those asymptomatic patients with antiphospholipid antibodies, and secondary to prevent recurrence in those who have suffered from previous thrombosis.
Keywords
Identifíquese
¿Aún no es suscriptor de la revista?
Comprar el acceso al artículo
Comprando el artículo el pdf del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio: 19,34 €
Teléfono para incidencias
De lunes a viernes de 9h a 18h (GMT+1) excepto los meses de julio y agosto que será de 9 a 15h