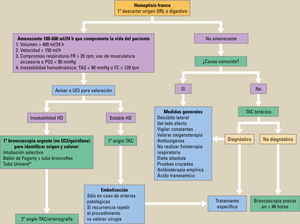
Se denomina hemoptisis a la expectoración de sangre procedente del árbol traqueobronquial. Las causas más frecuentes son las infecciones bronquiales, las bronquiectasias y el carcinoma broncogénico. Para el diagnóstico es preciso realizar una buena anamnesis y exploración física, así como cuantificar el volumen de hemoptisis en un recipiente graduado para identificar si se trata de una hemoptisis amenazante. En las hemoptisis no amenazantes se deberá realizar una analítica sanguínea, una radiografía de tórax y, si esta fuera patológica, una tomografía computarizada (TC) torácica, además de comenzar el tratamiento con medidas generales, antitusígenos y antibioterapia empírica. Ante una hemoptisis amenazante, será necesario avisar a la UCI y, posteriormente, realizar una angio-TC de arterias bronquiales de manera urgente para valorar embolizar aquellas que sean aberrantes. Si presentase inestabilidad hemodinámica, será preciso realizar una broncoscopia urgente previa a la intubación del paciente. La cirugía se reservará para casos seleccionados donde no se haya conseguido el control del sangrado.
Palabras clave
Hemoptysis is the expectoration of blood from the tracheobronchial tree. The most common causes are bronchial infections, bronchiectasis, and bronchogenic carcinoma. To diagnose it, it is necessary to take a good medical history and conduct a good physical examination as well as quantify the volume of hemoptysis in a graduated container to identify if it is life-threatening hemoptysis. In non-life-threatening hemoptysis, a blood test, a chest x-ray, and, if it is pathological, a computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest should be performed. In addition, treatment should be started with general and antitussive measures and empirical antibiotic treatment. When faced with life-threatening hemoptysis, it is necessary to notify the ICU and, later, conduct an emergency CT angiography of the bronchial arteries in order to evaluate whether to embolize those that are aberrant. If the patient presents with hemodynamic instability, it will be necessary to perform an emergency bronchoscopy prior to intubation of the patient. Surgery will be reserved for select cases in which it is not possible to control bleeding.
Keywords
Identifíquese
¿Aún no es suscriptor de la revista?
Comprar el acceso al artículo
Comprando el artículo el pdf del mismo podrá ser descargado
Teléfono para incidencias
De lunes a viernes de 9h a 18h (GMT+1) excepto los meses de julio y agosto que será de 9 a 15h