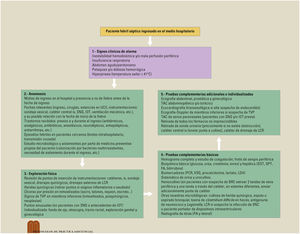
Los criterios diagnósticos de fiebre de origen desconocido son: temperatura ≥ 38,3°C medida en varias ocasiones, duración de más de tres semanas y en la que no se llega a un diagnóstico a pesar de un estudio de una semana con el enfermo hospitalizado.
EpidemiologíaMás del 50% de los pacientes con fiebre ingresados en el hospital presentan infección.
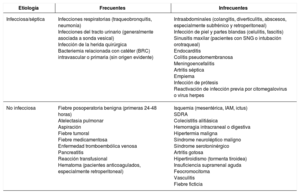
EtiologíaPuede ser de origen infeccioso (séptico) o no infeccioso.
Manifestaciones clínicas. Fiebre que puede acompañarse de hipotensión arterial, hipoperfusión tisular, insuficiencia respiratoria, encefalopatía, oliguria.
DiagnósticoLas consideraciones más importantes son la predisposición subyacente del paciente, las posibles complicaciones de la hospitalización, la situación epidemiológica y el entorno microbiológico del hospital.
TratamientoIniciar tratamiento antibiótico empírico con la mayor precocidad posible. La sospecha del foco, el perfil de resistencias y la susceptibilidad de los patógenos del área de hospitalización orientarán el tratamiento.
Palabras clave
The diagnostic criteria of fever of unknown origin are: temperature ≥ 38.3°C measured several times, duration of more than three weeks and in which a diagnosis is not reached despite a study of a week with the hospitalized patient.
EpidemiologyMore than 50% of patients with fever admitted to the hospital have an infection.
EtiologyMay be of infectious origin (septic) or non-infectious.
Clinical manifestationsFever that may be accompanied by hypotension, tissue hypoperfusion, respiratory failure, encephalopathy, oliguria.
DiagnosisThe most important considerations are the underlying predisposition of the patient, the possible complications of the hospitalization, the epidemiological situation and the microbiological environment of the hospital.
TreatmentInitiate empiric antibiotic treatment with the highest precocity possible. The suspicion of the focus, resistance profile and susceptibility of the pathogens of the hospitalization area will guide the treatment.
Keywords
Identifíquese
¿Aún no es suscriptor de la revista?
Comprar el acceso al artículo
Comprando el artículo el pdf del mismo podrá ser descargado
Teléfono para incidencias
De lunes a viernes de 9h a 18h (GMT+1) excepto los meses de julio y agosto que será de 9 a 15h